The Chinese Yuan’s share in global payments hit a record high in July 2024, seen as a milestone in the country’s efforts to fend off the hegemony of the U.S. dollar and increase its say in the international monetary system.
The Yuan kept its fourth-place spot in the ranking of payment currencies in July 2024, with its share of global transactions rising to 4.74 per cent from 4.61 per cent in June 2024. The increase was observed in data from the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (WIFT), the world’s largest interbank messaging service.
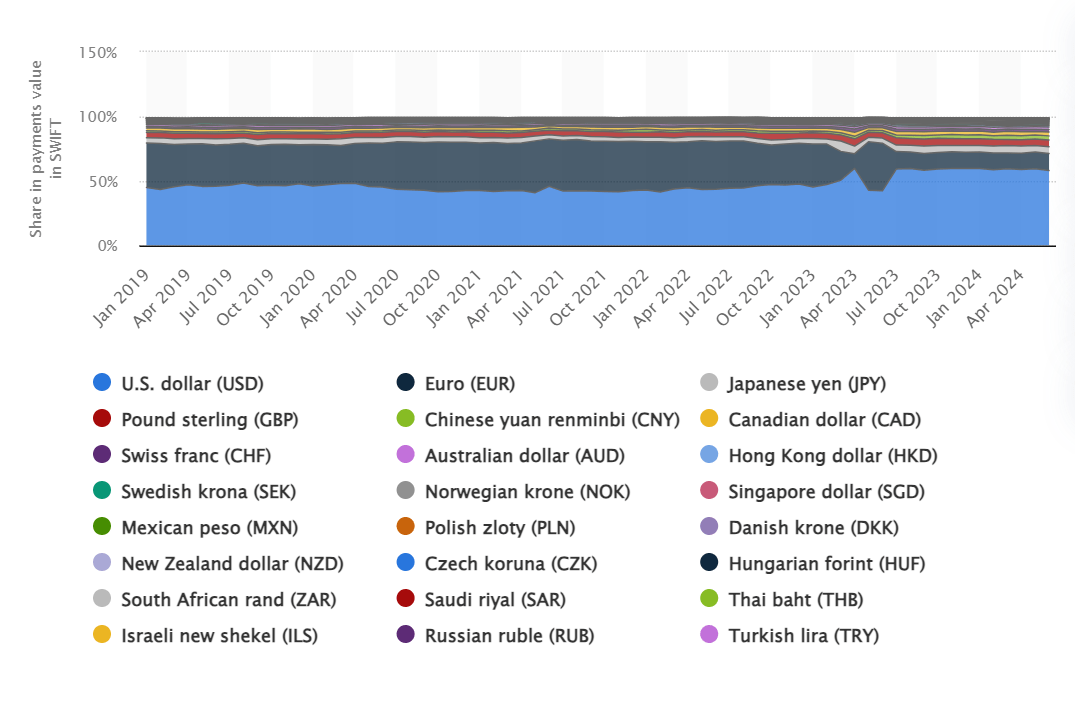

As of July 2024, global payments stand as follows:
- U.S. dollar – 47.8%
- The Euro – 22.5%
- The Starling Pound – 7%
- The Chinese Yuan – 4.74%
More than 11,000 banks and financial institutions rely on the SWIFT messaging network for financial transactions. In 2022, the SWIFT network registered an impressive average of 44.8 million messages daily, facilitating $150 trillion in transactions annually.
The U.S. dollar has maintained its dominance as the world’s reserve currency since SWIFT started tracking payments, but the use of the Chinese Yuan has risen steadily during the past decade.
Digital Yuan 🇨🇳 Transactions Increase 50x in One Year – Now Valued at Nearly $250 Billion
Despite these substantial figures, it is essential to note that the e-CNY’s circulation currently accounts for only a small fraction, specifically 0.16%, of the total amount of cash in… pic.twitter.com/z9F0TtkaIy
— BitKE (@BitcoinKE) July 29, 2023
When SWIFT began tracking the use of the Yuan in 2010, the currency accounted for less than 0.1 percent of global settlements. Since November 2023, the Yuan has become the fourth most active currency in the world, the first time since 2022 that it overtook the Yen.
In 2023, Yuan cross-border receipts and payments totaled 52.3 trillion Yuan ($7.2 trillion), an increase of 24.2 percent year-on-year, according to a recent People’s Bank of China (PBC) report on the Yuan’s internationalization.
As reported by BitKE, March 2023 was the standout month when China’s RMB Yuan overtook the U.S. dollar to become the most-used currency in the country’s cross-border transactions, according to data from China’s State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE).
MILESTONE: Chinese Yuan Surpasses U.S Dollar in Chinese Cross-Border Transactions for the First Time
By 2030, Yuan is predicted to become the 3rd most used currency in international payments.https://t.co/1ptvYr5h2L
— BitKE (@BitcoinKE) May 1, 2023
Overall, as it relates to China’s cross-border transactions for trade in goods, the proportion of Yuan settlements surged to 25 percent in 2023, up 7 percentage points from the 2022 level, read the report.
China’s efforts to reduce its reliance on the U.S. dollar in international trade are said to have accelerated due to the sanctions imposed by Western countries against Russia, a significant global energy producer and exporter. These sanctions have disrupted global trade flows and increased the risk of financial transactions denominated in U.S. dollars prompting China to seek alternatives.
China is not alone in these efforts, with its partners in the BRICS group of countries having taken similar measures to boost cross-border trade using their currencies. These include India, Egypt, and South Africa.
BRICS | BRICS Countries Declare to Enhance Trade Settlement Using Local Currencies
The Johanessburg II declaration stated: “We task our Finance Ministers and/or Central Bank Governors, as appropriate, to consider the issue of local currencies, payment instruments and platforms… pic.twitter.com/ZU1p1KHtWt
— BitKE (@BitcoinKE) August 31, 2023
Follow us on X for the latest posts and updates
Join and interact with our Telegram community
________________________________________
________________________________________









